
Node.js for Rails developers, Part 6b (MongoDB Datastore)
Published: 2016-04-09
By: MJ Rossetti

Published: 2016-04-09
By: MJ Rossetti
This post is part of a series for Rails developers who want to get started with Node.js. After enabling basic navigation, it’s time to enable database functionality. This post describes the process of connecting the application to a MongoDB datastore.
Follow these instructions to install MongoDB on your local machine using Homebrew, if necessary.
To interface with MongoDB, we’ll use the Mongoose module to specify the schema and execute queries. Let’s install it now.
npm install mongoose --save
Mongoose includes Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) capabilities like ActiveRecord does. This means there are models with Mongoose. Let’s create them now.
Create models.
mkdir -p app/models
touch app/models/robot.js
Edit app/models/robot.js according to the following template:
// app/models/robot.js
var mongoose = require( 'mongoose' );
var Schema = mongoose.Schema;
var RobotSchema = new Schema(
{
name : {
type: String,
required: true
},
description : {
type: String,
required: true
}
},
{
timestamps: { // include timestamp attributes in the schema and automatically assign values on create and update, respectively
createdAt: 'created_at', // rename from createdAt
updatedAt: 'updated_at' // rename from updatedAt
}
}
);
module.exports = mongoose.model('Robot', RobotSchema);
Add a new database connection file.
touch db.js
Edit db.js according to the following template:
// db.js
var mongoose = require( 'mongoose' );
var mongoConnectionString = process.env.MONGODB_URI || 'mongodb://localhost/robots_dev';
mongoose.connect(mongoConnectionString); // establishes a database connection which may in some cases need to be manually closed ... use db.disconnect();
module.exports = mongoose;
Tell the web server to start a database connection. Edit app.js to include the following code:
// app.js
// ...
var db = require("./db") // MONGO ADDITION! starts a new mongoose connection
// ...
Create a new database population script.
touch db/seed.js
Edit db/seed.js according to the following template:
// db/seed.js
var db = require("../db"); // starts a mongoose connection
var Robot = require("../app/models/robot");
var robots = [
{name:"c3po", description:"specializes in language translation"},
{name:"r2d2", description:"holds a secret message"},
{name:"bb8", description:"rolls around"}
];
Robot.find(function (err, bots) {
if (err) return console.error(err);
console.log("FOUND", bots.length, "ROBOTS TO BE DELETED")
Robot.remove(bots, function (err) {
if (err) return console.error(err);
console.log("DELETED")
Robot.create(robots, function (err, new_bots) {
console.log(new_bots)
db.disconnect(); // close the connection, else it will keep running, which is appropriate for when the web server runs, but not for a script like this.
});
});
});
Run it.
node db/seed.js
At this point, you should be able to login to MongoDB to confirm existence of a database called robots_dev, a collection called robots, and three example robot records.
mongo
> show dbs
> use robots_dev
> show collections
> db.robots.find().pretty()
> exit
We want the application to display robots from the database, not from a hard-coded variable. We also want to be able to use our views to add, edit, and delete robots from the database. Let’s connect our robots controller actions to the database.
Modify app/controllers/robots_controller.js according to the following template:
// app/controllers/robots_controller.js
var express = require('express');
var router = express.Router();
var Robot = require("../models/robot");
var mongooseError = require("../helpers/mongoose_error")
var create_robot_path = '/robots/';
function updateRobotPath(robot_id){
return '/robots/'+robot_id+'/update';
};
/* INDEX */
router.get('/robots', function(req, res, next) {
Robot.find( function (err, bots) {
console.log("LIST", bots.length, "ROBOTS:", bots);
res.render('robots/index', {
page_title: 'Robots',
robots: bots.reverse()
});
});
});
/* CREATE */
router.post('/robots', function(req, res, next) {
console.log("CAPTURE FORM DATA:", req.body)
var robot_name = req.body.robotName;
var robot_description = req.body.robotDescription;
var bot = new Robot({name: robot_name, description: robot_description});
bot.save(function(saveErr, bot_id) {
if (saveErr){
console.log(saveErr);
var error_messages = mongooseError.toMessages(saveErr);
req.flash('danger', error_messages);
res.render('robots/new', {
page_title: 'Add a new Robot',
form_action: create_robot_path,
robot: {name: robot_name, description: robot_description} // pass-back attempted values to the form in case one was not blank
});
} else {
console.log("CREATE ROBOT", bot)
req.flash('success', 'Created a New Robot named '+robot_name );
res.redirect('/robots')
};
});
});
/* NEW */
// this must come above the SHOW action else express will think the word 'new' is the :id
router.get('/robots/new', function(req, res, next) {
console.log("NEW ROBOT")
res.render('robots/new', {
page_title: 'Add a new Robot',
form_action: create_robot_path
});
});
/* SHOW */
router.get('/robots/:id', function(req, res, next) {
var robot_id = req.params.id;
Robot.findById(robot_id, function(err, bot) {
if (err){
console.log("COULDN'T SHOW ROBOT #"+robot_id);
console.log(err);
var error_messages = mongooseError.toMessages(err);
req.flash('danger', error_messages);
res.redirect('/robots');
} else {
console.log("SHOW ROBOT:", bot);
res.render('robots/show', {
page_title: 'Robot #'+bot.id,
robot: bot
});
};
});
});
/* EDIT */
router.get('/robots/:id/edit', function(req, res, next) {
var robot_id = req.params.id;
Robot.findById(robot_id, function(err, bot) {
console.log("EDIT ROBOT", bot);
res.render('robots/edit', {
page_title: 'Edit Robot #'+bot.id,
robot: bot,
form_action: updateRobotPath(bot.id)
});
});
});
/* UPDATE */
router.post('/robots/:id/update', function(req, res, next) {
console.log("CATURED FORM DATA", req.body)
var robot_id = req.params.id;
var robot_name = req.body.robotName;
var robot_description = req.body.robotDescription;
Robot.findById(robot_id, function(err, bot) {
bot.name = req.body.robotName
bot.description = req.body.robotDescription
bot.save(function(saveErr, new_bot) {
if (saveErr){
console.log(saveErr)
var error_messages = mongooseError.toMessages(saveErr)
req.flash('danger', error_messages);
res.render('robots/edit', {
page_title: 'Edit Robot #'+robot_id,
form_action: updateRobotPath(robot_id),
robot: {name: robot_name, description: robot_description} // pass-back attempted values to the form in case one was not blank
});
} else {
console.log("UPDATED ROBOT", new_bot)
req.flash('success', 'Updated Robot #'+new_bot._id );
res.redirect('/robots')
};
});
});
});
/* DESTROY */
router.post('/robots/:id/destroy', function(req, res, next) {
var robot_id = req.params.id;
Robot.findById(robot_id, function(err, bot) {
bot.remove( function(rmErr, removed_bot) {
if (rmErr) {
console.log("COULDN'T DELETE ROBOT #", bot_id);
req.flash('danger', "Couldn't delete Robot #"+bot_id );
var error_messages = mongooseError.toMessages(rmErr);
req.flash("danger", error_messages)
} else {
console.log("DELETED ROBOT", removed_bot);
req.flash('success', 'Deleted Robot #'+removed_bot._id );
}
res.redirect('/robots');
});
});
});
module.exports = router;
You’ll notice references to a helper file called mongoose_error. Create it now.
touch app/helpers/mongoose_error.js
Edit app/helpers/mongoose_error.js according to the following template:
// app/helpers/mongoose_error.js
var exports = module.exports = {};
// Transform mongoose error object into error message(s).
//
// @param [ValidationError] err A mongoose error like...
//
// {
// message: 'Note validation failed',
// name: 'ValidationError',
// errors:{
// description:{
// message: 'Path `description` is required.',
// name: 'ValidatorError',
// properties: [Object],
// kind: 'required',
// path: 'description',
// value: ''
// },
// title:{
// message: 'Path `name` is required.',
// name: 'ValidatorError',
// properties: [Object],
// kind: 'required',
// path: 'title',
// value: ''
// }
// }
// }
//
// ... or like ...
//
// {
// message: 'Cast to ObjectId failed for value "abc" at path "_id"',
// name: 'CastError',
// kind: 'ObjectId',
// value: 'abc',
// path: '_id',
// reason: undefined
// }
//
// @return [Array] error_messages
exports.toMessages = function(err){
if (err.name == "ValidationError") {
var errors = err.errors
var error_messages = Object.keys(errors).map(function(k) {
var error = errors[k]
return error.name+': '+error.path+' is '+error.kind //> ValidatorError: description is required
});
} else if (err.name == "CastError") {
var error_messages = ["Sorry, couldn't find a robot with that identifier..."]
} else {
var error_messages = ["Oops, something unexpected has happened..."]
};
return error_messages //> ["ValidatorError: description is required", "ValidatorError: title is required"]
};
Revisit the app in your browser.
At this point you should be able to use the front-end interface to create, read, update, and display robots.
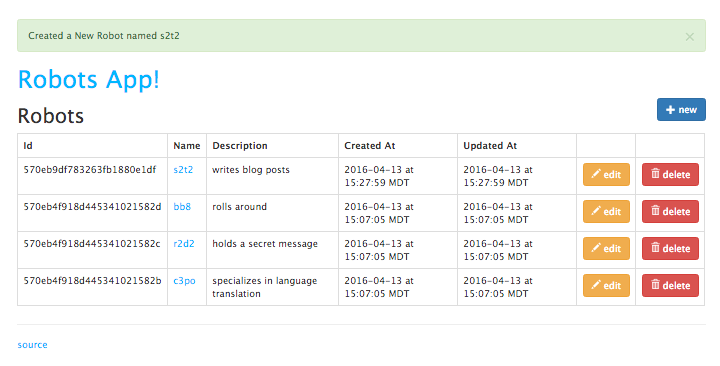
Nice job. After a few more steps, we’ll be ready to push this application to production.